Nested sampling is an alternative to MCMC methods that overcomes two of its major struggles:
Calculates the evidence, which serves for model selection
Works well with multimodal problems
Nested sampling is based on breaking the posterior into nested slices with increasing likelihoods
The samples are then recombined with appropriate weights to yield a posterior estimate
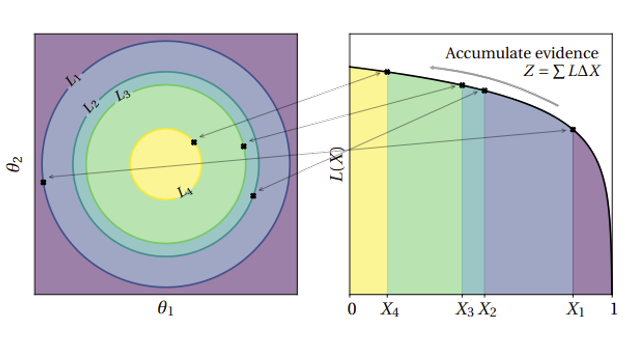
“Nested sampling for physical scientists”, Ashton et. al. (2022)
Optional 💽
🖱️Right-click and select “Save link as” to download the exercise HERE 👈 so you can work on it locally on your computer
import numpy as np
# Problem definition
from probeye.definition.inverse_problem import InverseProblem
from probeye.definition.forward_model import ForwardModelBase
from probeye.definition.distribution import Normal, Uniform
from probeye.definition.sensor import Sensor
from probeye.definition.likelihood_model import GaussianLikelihoodModel
from probeye.definition.correlation_model import ExpModel
# Inference
from probeye.inference.dynesty.solver import DynestySolverProblem setup¶
# Fixed parameters
I = 1e9 # mm^4
L = 10_000 # mm
# Measurements
x_sensors = [2500, 5000] # mm (always from lower to higher, bug in inv_cov_vec_1D in tripy)
d_sensors = [35, 50] # mm
sigma_model = 2.5 # mm
pearson = 0.5
l_corr = -np.abs(x_sensors[1] - x_sensors[0]) / np.log(pearson) # mm (assuming exponential correlation)
# Prior
E_mean = 60 # GPa
E_std = 20 # GPa
Q_mean = 60 # kN
Q_std = 30 # kN
Q_loc_low = 0 # mm
Q_loc_high = 10000 # mmDefine forward model¶
def beam_deflection(E, Q, a, x): # a is load position, x is sensor position
if x < a:
b = L - a
return Q * b * x * (L ** 2 - b ** 2 - x ** 2) / (6 * E * I * L)
return Q * a * (L - x) * (2 * L * x - x ** 2 - a ** 2) / (6 * E * I * L)class BeamModel(ForwardModelBase):
def interface(self):
self.parameters = ["E", "Q", "a"]
self.input_sensors = Sensor("x")
self.output_sensors = Sensor("y", std_model="sigma")
def response(self, inp: dict) -> dict:
E = inp["E"]
Q = inp["Q"]
a = inp["a"]
x = inp["x"]
return {"y": [beam_deflection(E, Q, a, float(x[0])), beam_deflection(E, Q, a, float(x[1]))]} # float() needed, probably a bug in probeyeDefine inverse problem¶
# Instantiate the inverse problem
problem = InverseProblem("Beam model with two sensors", print_header=False)
# Add latent parameters
problem.add_parameter(
"E",
tex="$E$",
info="Elastic modulus of the beam (GPa)",
prior=Normal(mean=E_mean, std=E_std),
)
problem.add_parameter(
"Q",
tex="$Q$",
info="Load applied to the beam (kN)",
prior=Normal(mean=Q_mean, std=Q_std),
)
problem.add_parameter(
"a",
tex="$a$",
info="Position of the load (mm)",
prior=Uniform(low=Q_loc_low, high=Q_loc_high)
)
# Add fixed parameters
problem.add_parameter(
"sigma",
tex="$\sigma$",
info="Standard deviation of the model error (mm)",
value=sigma_model,
)
problem.add_parameter(
"l_corr",
tex="$l_{corr}$",
info="Correlation length of the model error (mm)",
value=l_corr,
)
# Add measurement data
problem.add_experiment(
name="TestSeries_1",
sensor_data={"x": x_sensors, "y": d_sensors}
)
# Add forward model
problem.add_forward_model(BeamModel("BeamModel"), experiments="TestSeries_1")
# Add likelihood model
likelihood_model = GaussianLikelihoodModel(
experiment_name="TestSeries_1",
model_error="additive",
correlation=ExpModel(x="l_corr")
)
problem.add_likelihood_model(likelihood_model)
## Write your code where the three dots are
dynesty_solver = DynestySolver(..)
inference_data = dynesty_solver.run(...)Static method¶
## Write your code where the three dots are
dynesty_solver = DynestySolver(..)
inference_data = dynesty_solver.run(...)Increasing the number of live points¶
## Write your code where the three dots are
dynesty_solver = DynestySolver(..)
inference_data = dynesty_solver.run(...)Complete Code! 📃💻
Here’s the complete code that you would run in your PC:
import numpy as np
# Problem definition
from probeye.definition.inverse_problem import InverseProblem
from probeye.definition.forward_model import ForwardModelBase
from probeye.definition.distribution import Normal, Uniform
from probeye.definition.sensor import Sensor
from probeye.definition.likelihood_model import GaussianLikelihoodModel
from probeye.definition.correlation_model import ExpModel
# Inference
from probeye.inference.dynesty.solver import DynestySolver
# Fixed parameters
I = 1e9 # mm^4
L = 10_000 # mm
# Measurements
x_sensors = [2500, 5000] # mm (always from lower to higher, bug in inv_cov_vec_1D in tripy)
d_sensors = [35, 50] # mm
sigma_model = 2.5 # mm
pearson = 0.5
l_corr = -np.abs(x_sensors[1] - x_sensors[0]) / np.log(pearson) # mm (assuming exponential correlation)
# Prior
E_mean = 60 # GPa
E_std = 20 # GPa
Q_mean = 60 # kN
Q_std = 30 # kN
Q_loc_low = 0 # mm
Q_loc_high = 10000 # mm
def beam_deflection(E, Q, a, x): # a is load position, x is sensor position
if x < a:
b = L - a
return Q * b * x * (L ** 2 - b ** 2 - x ** 2) / (6 * E * I * L)
return Q * a * (L - x) * (2 * L * x - x ** 2 - a ** 2) / (6 * E * I * L)
class BeamModel(ForwardModelBase):
def interface(self):
self.parameters = ["E", "Q", "a"]
self.input_sensors = Sensor("x")
self.output_sensors = Sensor("y", std_model="sigma")
def response(self, inp: dict) -> dict:
E = inp["E"]
Q = inp["Q"]
a = inp["a"]
x = inp["x"]
return {"y": [beam_deflection(E, Q, a, float(x[0])), beam_deflection(E, Q, a, float(x[1]))]} # float() needed, probably a bug in probeye
# Instantiate the inverse problem
problem = InverseProblem("Beam model with two sensors", print_header=False)
# Add latent parameters
problem.add_parameter(
"E",
tex="$E$",
info="Elastic modulus of the beam (GPa)",
prior=Normal(mean=E_mean, std=E_std),
)
problem.add_parameter(
"Q",
tex="$Q$",
info="Load applied to the beam (kN)",
prior=Normal(mean=Q_mean, std=Q_std),
)
problem.add_parameter(
"a",
tex="$a$",
info="Position of the load (mm)",
prior=Uniform(low=Q_loc_low, high=Q_loc_high)
)
# Add fixed parameters
problem.add_parameter(
"sigma",
tex="$\sigma$",
info="Standard deviation of the model error (mm)",
value=sigma_model,
)
problem.add_parameter(
"l_corr",
tex="$l_{corr}$",
info="Correlation length of the model error (mm)",
value=l_corr,
)
# Add measurement data
problem.add_experiment(
name="TestSeries_1",
sensor_data={"x": x_sensors, "y": d_sensors}
)
# Add forward model
problem.add_forward_model(BeamModel("BeamModel"), experiments="TestSeries_1")
# Add likelihood model
likelihood_model = GaussianLikelihoodModel(
experiment_name="TestSeries_1",
model_error="additive",
correlation=ExpModel(x="l_corr")
)
problem.add_likelihood_model(likelihood_model)
#Dynamic method
dynesty_solver = DynestySolver(problem, show_progress=True)
inference_data = dynesty_solver.run(estimation_method='dynamic', nlive=250)
#Static method
dynesty_solver = DynestySolver(problem, show_progress=True)
inference_data = dynesty_solver.run(estimation_method='static', nlive=250)
#Increse number of live points
dynesty_solver = DynestySolver(problem, show_progress=True)
inference_data = dynesty_solver.run(estimation_method='static', nlive=1000)